After more than 70 years, the Ford Motor Co. finally has an architectural centerpiece.
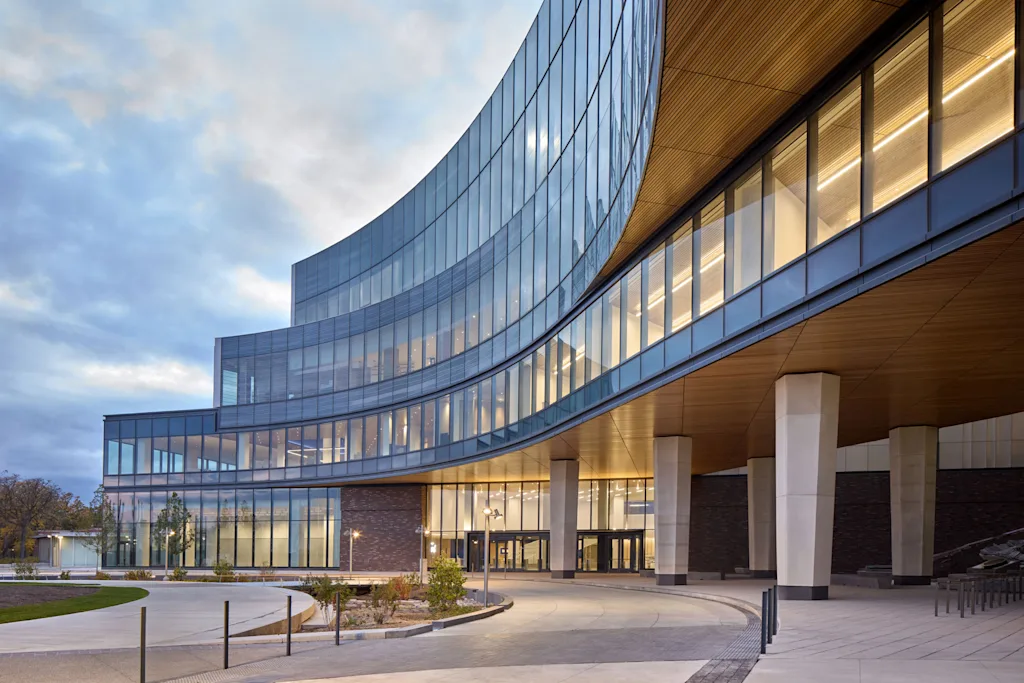
The automaker’s new global headquarters has officially opened in Dearborn, Michigan, just outside Detroit and within eyeshot of some of the main facilities that have sustained the company for more than a century. Covering 2.1 million square feet and designed by the architecture and design firm Snøhetta, the new building sprawls across four circuitous stories. Getting from one side to another is a trek.
During a two-hour walking tour of the building, a week ahead of its official opening, I traversed at most a quarter of the overall space. This immense size is the building’s strength, as it allows the company to bring much of its executive, engineering, design, and fabrication teams under one (very large) roof for the first time. About 2,000 Ford employees work there now, with around 4,500 expected by 2027.
Jim Dobleske, CEO of Ford Land, the company’s real estate arm, says the headquarters was designed to enable collaboration and a more flexible approach to office work—two post-pandemic prerequisites. More importantly, the building is meant to streamline how different arms of the company work together, using proximity, shared resources, and the simplicity of a single building to break down historic silos.
“It’s not just a building,” Dobleske says, walking through its airy front lobby. “It’s a tool.”
The Ford of 2025 is a different company than its mid-20th-century self, then still heavily influenced by the top-down approach of founder Henry Ford, even years after his death. Still, there are strands of the corporate DNA that have carried through over the company’s 122-year history. Ford has historically been a deeply stratified corporation, with a longstanding emphasis on command and control. Today, its evolving architecture is a reflection of a company that’s reconsidering its approach and priming itself for a particularly dynamic era in the history of automaking.

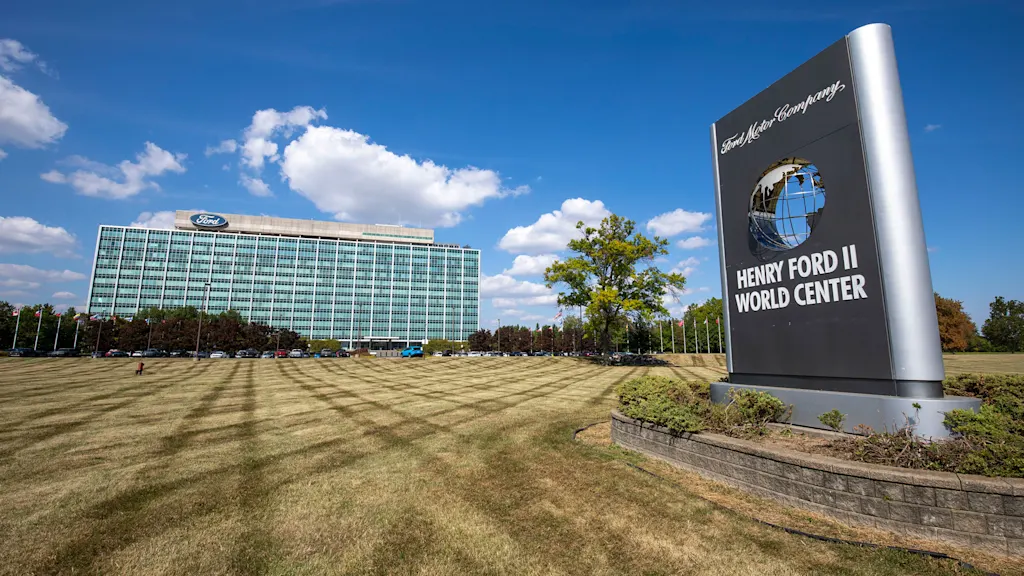
The new building sits 2 miles away from Ford’s former headquarters, a 12-story modernist box known as the “Glass House,” which has been the buttoned-up main office for 2,000 of the corporation’s higher-ups since it opened in 1956. Located on the other side of a highway cloverleaf and moated by a wide belt of lawn and parking lots, the building was emblematic of Ford’s corporate architectural sensibility, as well as its corporate structure.

The new building is designed as the new hub of an increasingly concentrated campus of Ford buildings, situated within walking distance to an estimated 14,000 Ford employees, each of whom can use the building’s common spaces, bookable meeting rooms, and 1,000-seat food court. That includes staff at the product development center, engineers from the recently renovated Ford Engineering Lab across the street, and researchers in its components laboratory.
“It’s the most horizontally and vertically integrated building I know of,” says Craig Dykers, cofounder of Snøhetta and architect of the building. His firm also created the campus master plan that has reshaped the corporate landscape of Ford.
During the tour, Dykers stood near a window and pointed out the buildings and facilities in the area that are all part of the Ford machine. “We took a lot of facilities that were spread all over and pushed them together,” he says.


Inside the HQ
A few finishing touches remain before the project is officially complete in 2027—including parking garages that will be tucked beneath additional performative landscape that’s able to divert and clean stormwater and building runoff—but the building is already humming with activity.
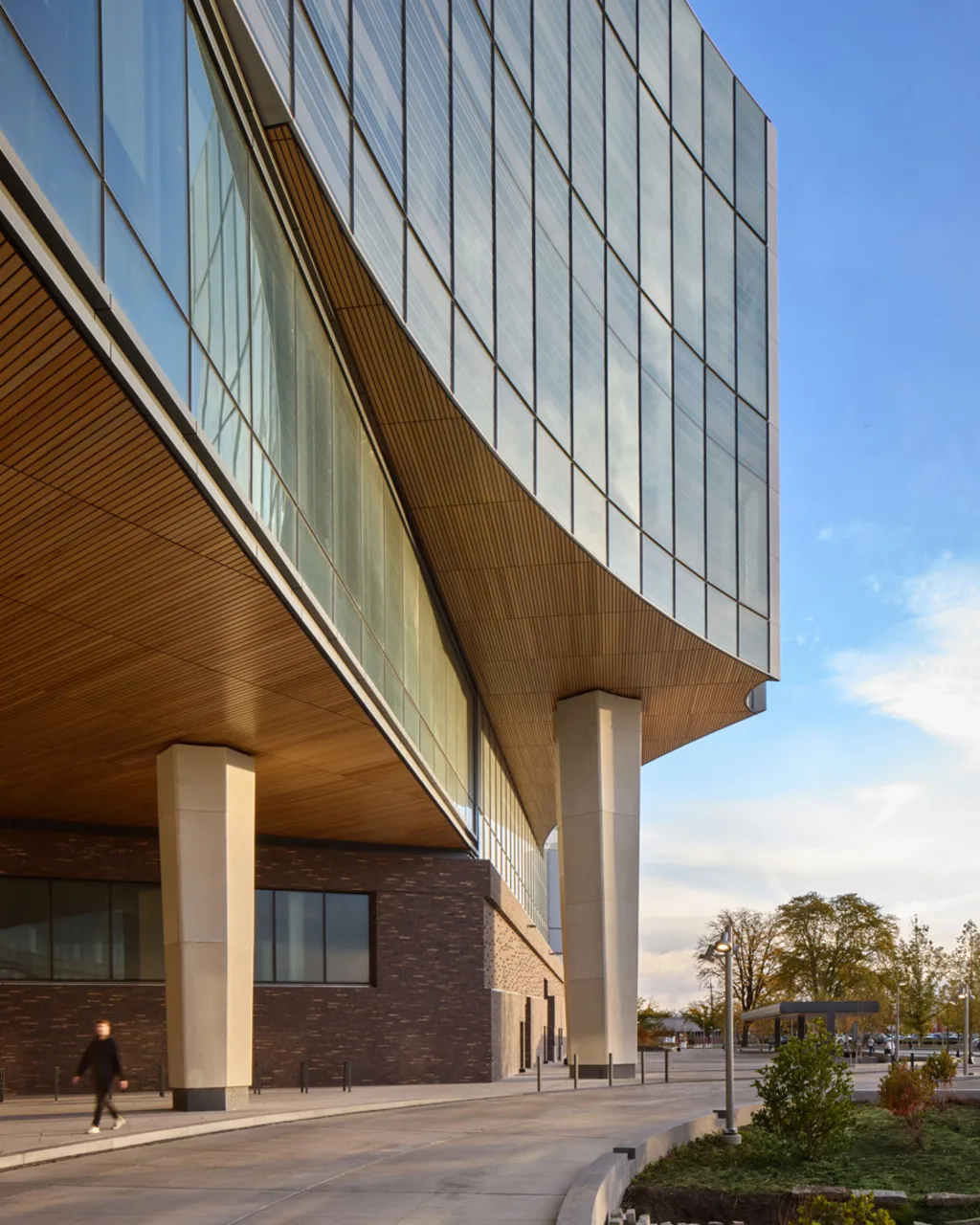
From the outside, Ford’s new headquarters is a gleaming spaceship of a building, with scalloped edges covered by flat and subtly shaded glass. The building’s plan, seen from overhead, is of three hexagons arranged into a kind of triangle, with spaces cut out from their centers to create large internal courtyards.
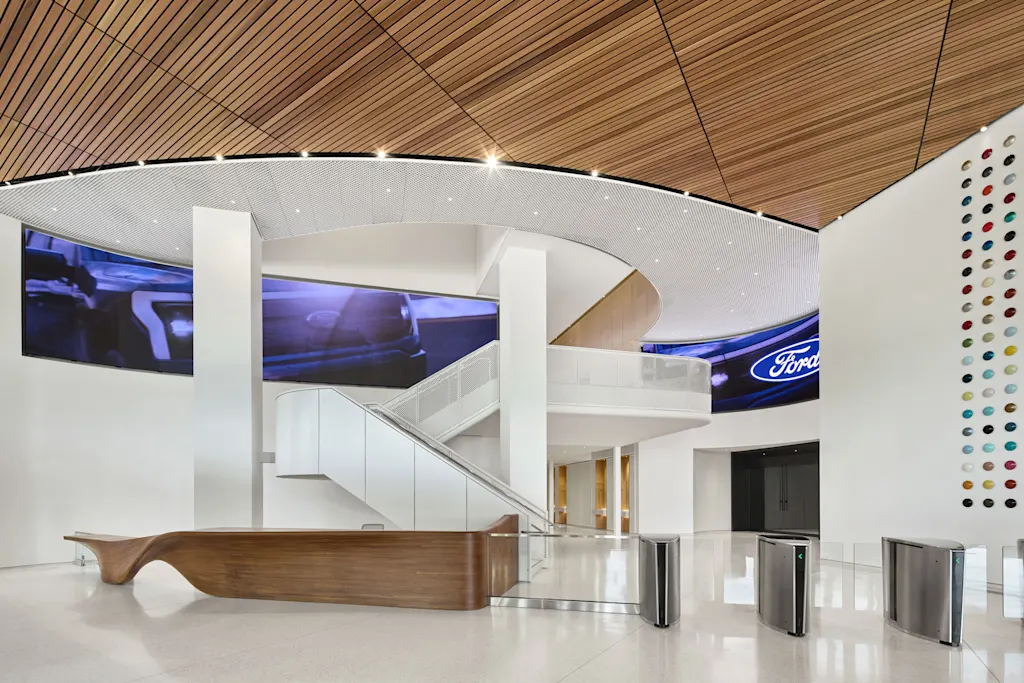

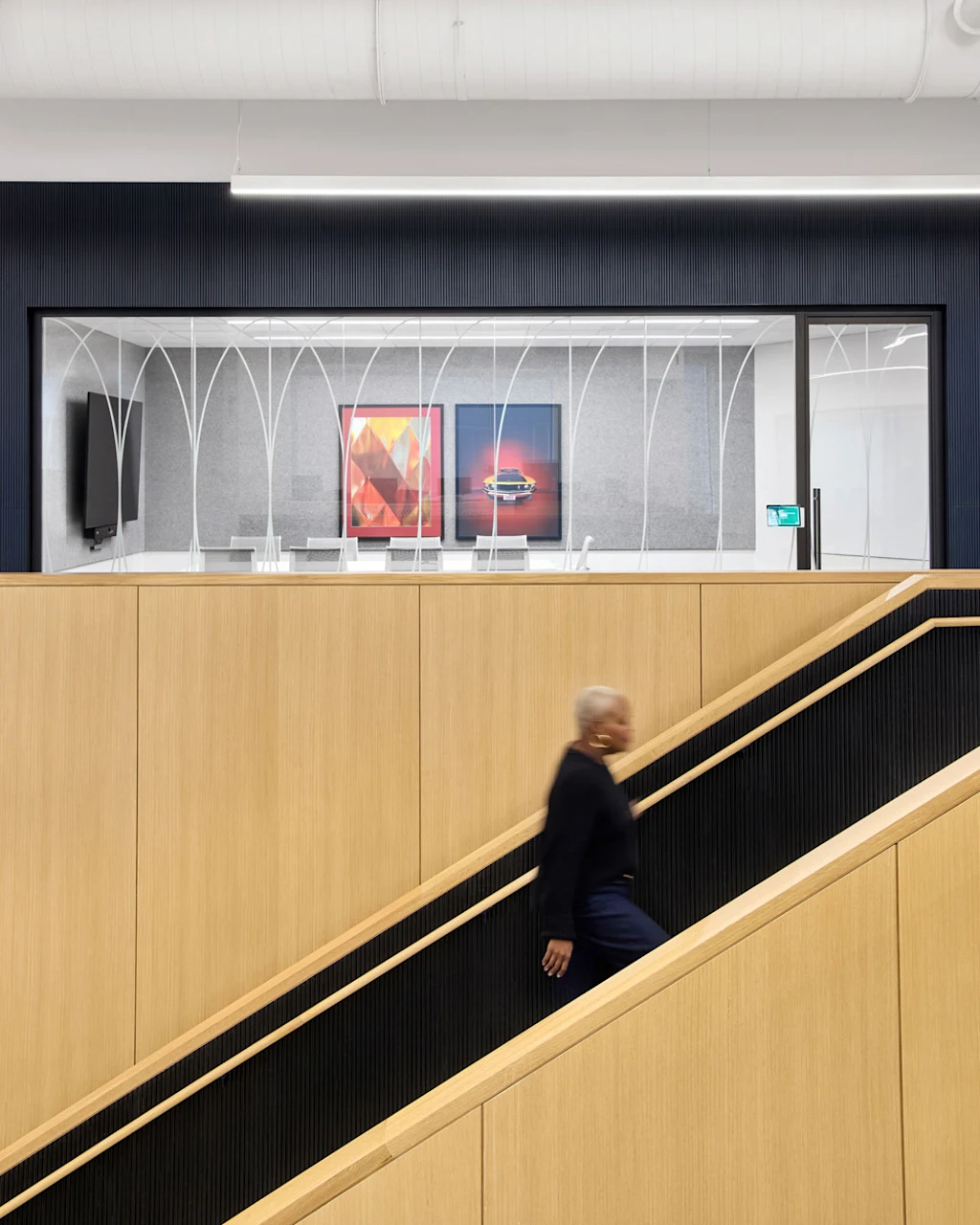
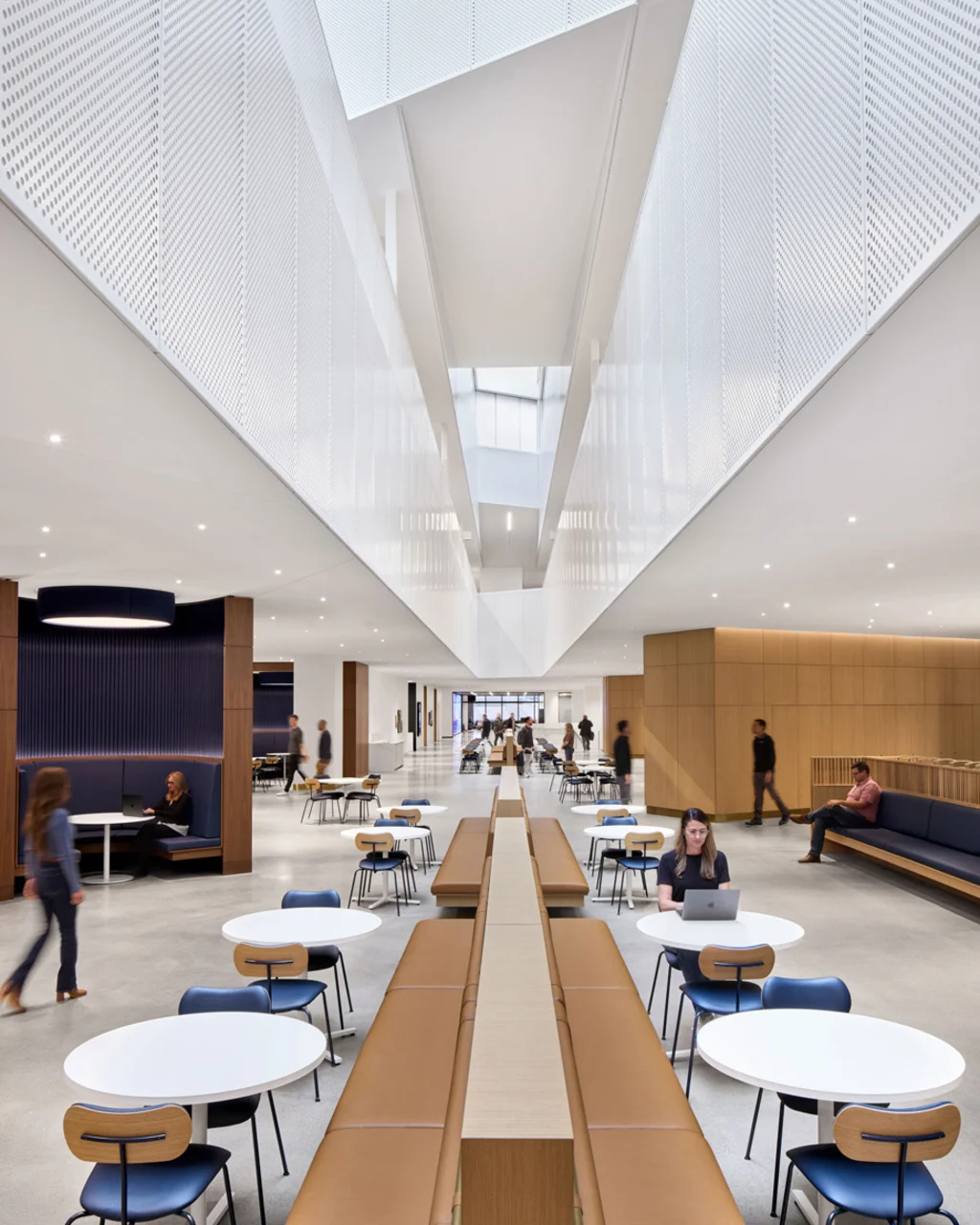
Walking through the building, its sheer size is hard to fully grasp, and parts can feel disorienting. But there are even more places where a corner is turned, or a stairway is climbed, to reveal a view down a corridor that resets the internal map. Glimpses can often be seen of the four accessible courtyard spaces, each of which has been designed by Snøhetta to reflect a different regional habitat. The largest courtyard, inspired by the Great Lakes, features cascades of stone, two bookable meeting canopies, and large sliding doors that connect to seating in the building’s dining area.

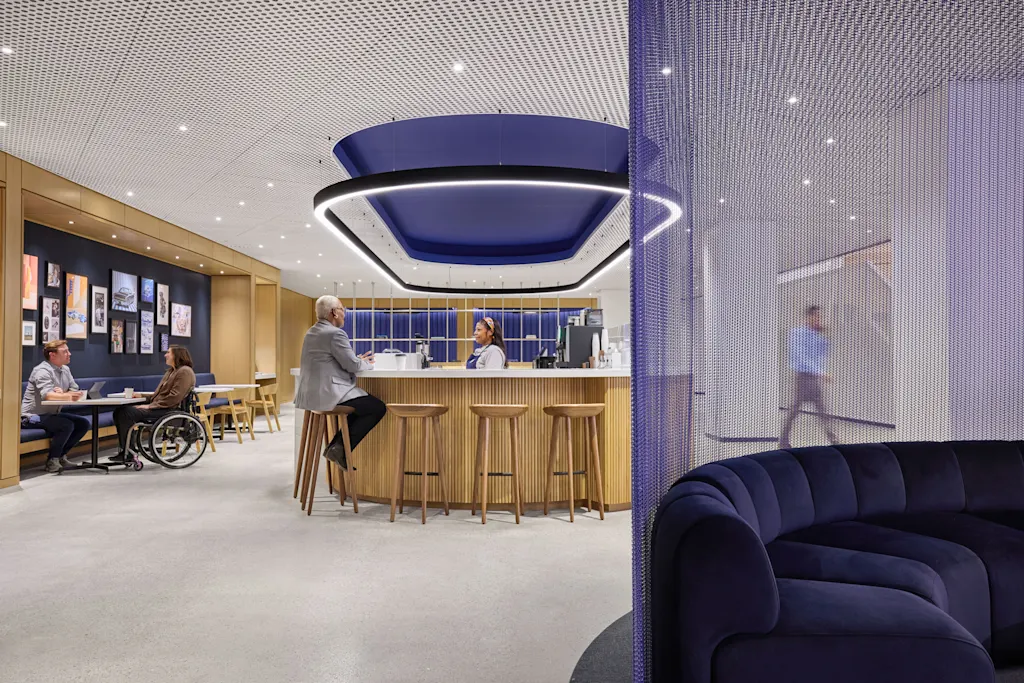
This area is accessible to any Ford employee, even those not working within the headquarters building. Jennifer Kolstad, global design and brand director at Ford Land, says it’s part of the company’s effort to rethink its global real estate portfolio and make more spaces more accessible for different types of work, be it a lunch meeting or a heads-down cram session in a private booth. It’s a far cry from the culture of desks that long reigned at Ford, she says.

The design, informed by Kolstad’s deep experience in interior architecture and hospitality design, is intended to create a human scale. “The challenge of this is 2.1 million square feet at human scale,” she says. Working closely with the architects at Snøhetta, Ford’s design team integrated hotel lobby-style seating across the building, as well as grand staircases that double as seating for informal meetings or large gatherings.

The right amount of transparency
With so many parts of the company situated in this one building, including highly sensitive operations like the development of new car designs, there was a challenge in making the building accessible without completely blowing the doors open. One solution has been the creation of 14 “arrival areas” outside the secured doors of specific business functions. These are café-like seating areas and meeting spaces where people can gather for coffee or a meeting without having to navigate through secured parts of the building.


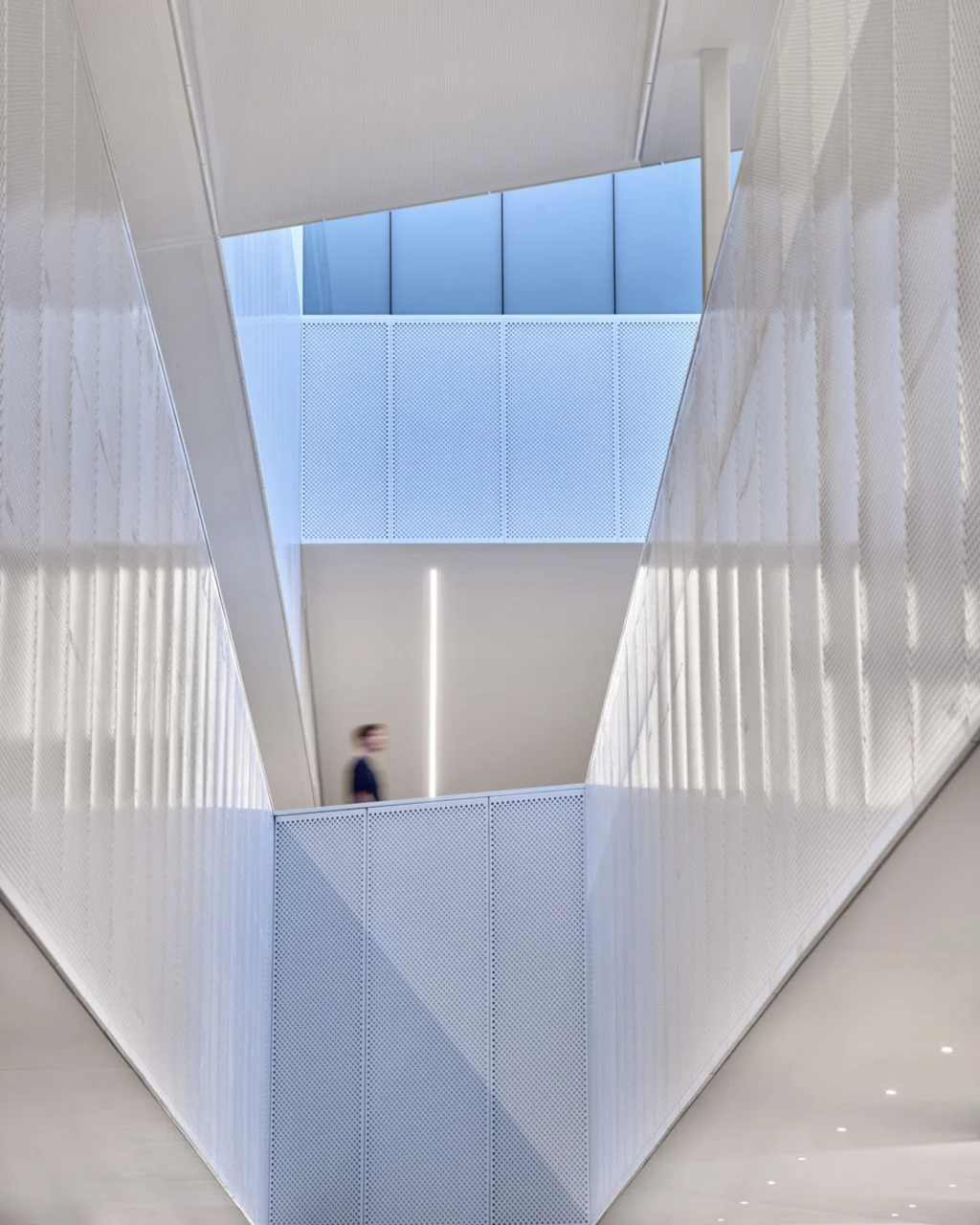
This attempt at openness extends to the architecture itself. Walking through the straight spine that runs between the three hexagons of the building, Dykers points up at a narrow atrium that runs through the top three floors of the building. A skylight pours light down, and people on each floor can get glimpses of what’s happening elsewhere, even if they don’t have the badge to get them through the door.
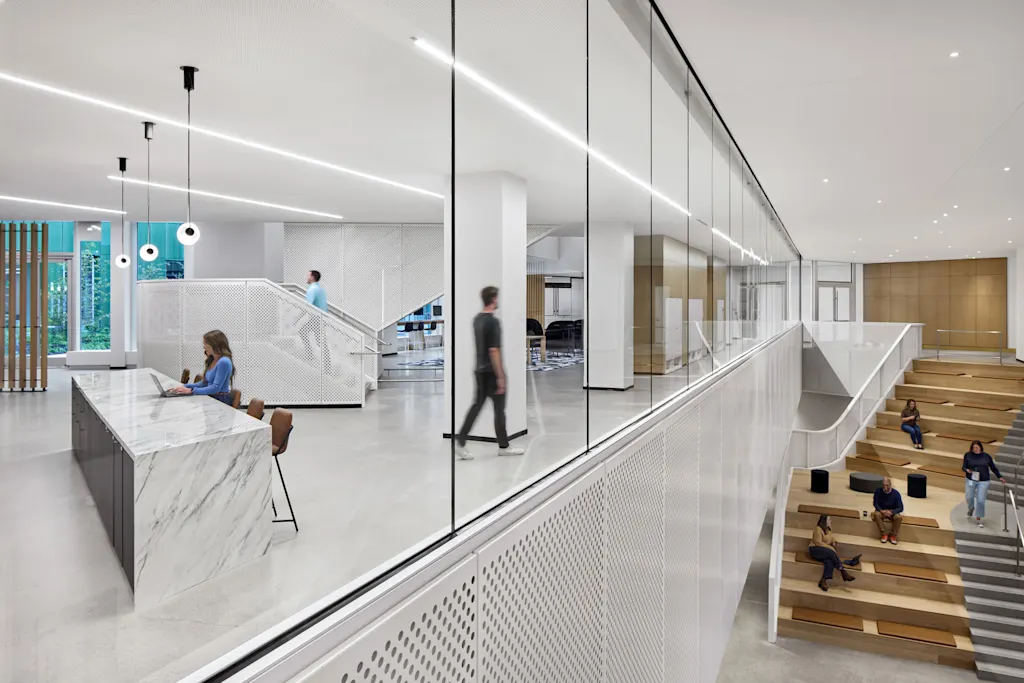

There are four different levels of security in the building, according to Ford Land’s Dobleske, including one for the top floor where there are several design studios that often move full-scale car models and properties across the building’s 22-inch-thick concrete floors. A corporate spy’s dream, these concepts and nascent designs are cleverly obscured behind frosted glass and partitions, while still allowing the skylight and atrium to spread light and views to the floors below. “We still want people to be able to see people and properties moving through the building,” Dobleske says.
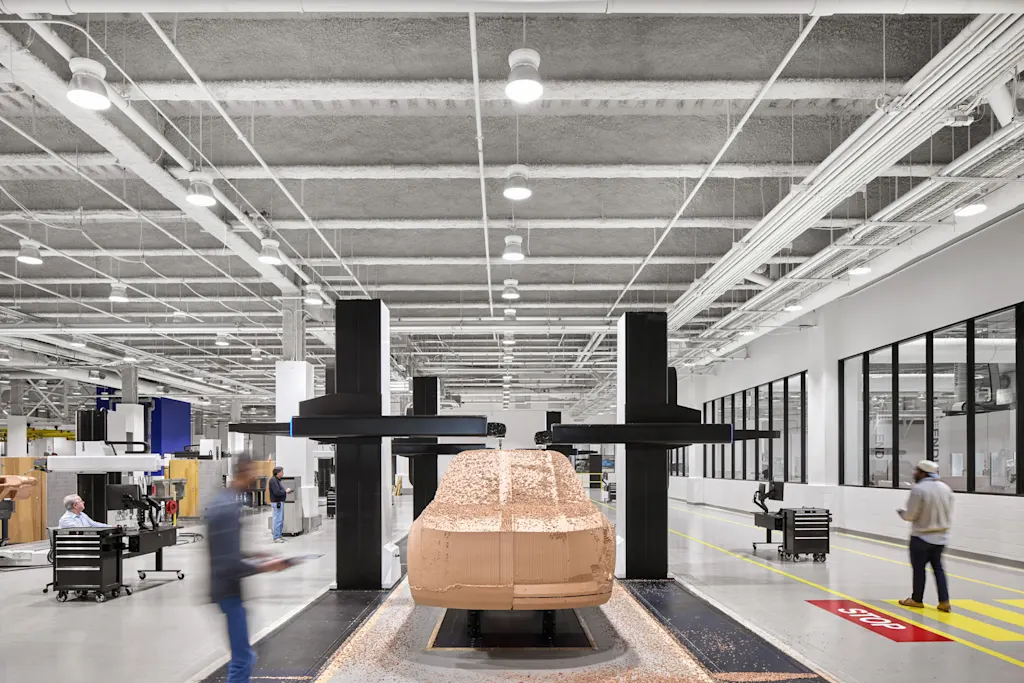

But there’s a limit to that spirit of transparency, especially when it comes to product development. The design studios are located on the building’s two top floors, including spaces along window-lined edges of the building that could potentially offer views to prying eyes outside.
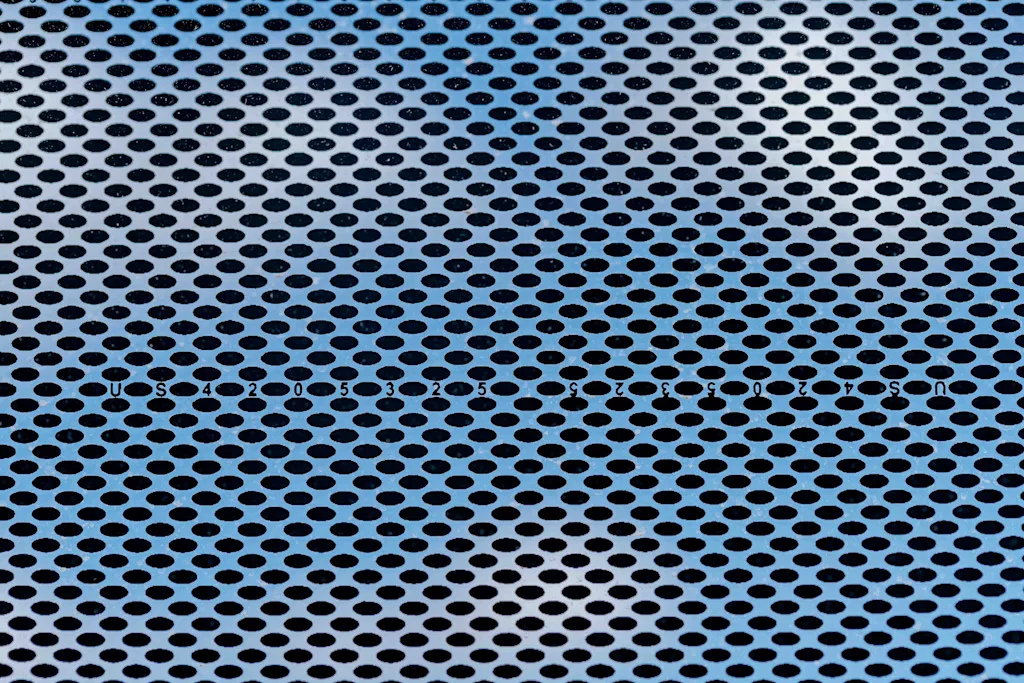
To allow light in while maintaining privacy, the glass that wraps the entire building has been treated with a specially designed frit patterning that obscures the view. In a nod to Ford’s famous logo, the frit is made up of millions of tiny ovals—black on the interior side of the window and white on the exterior—to help manage heat inside while also preventing design secrets from spilling out. “It took us over a year to develop that,” Dykers says.
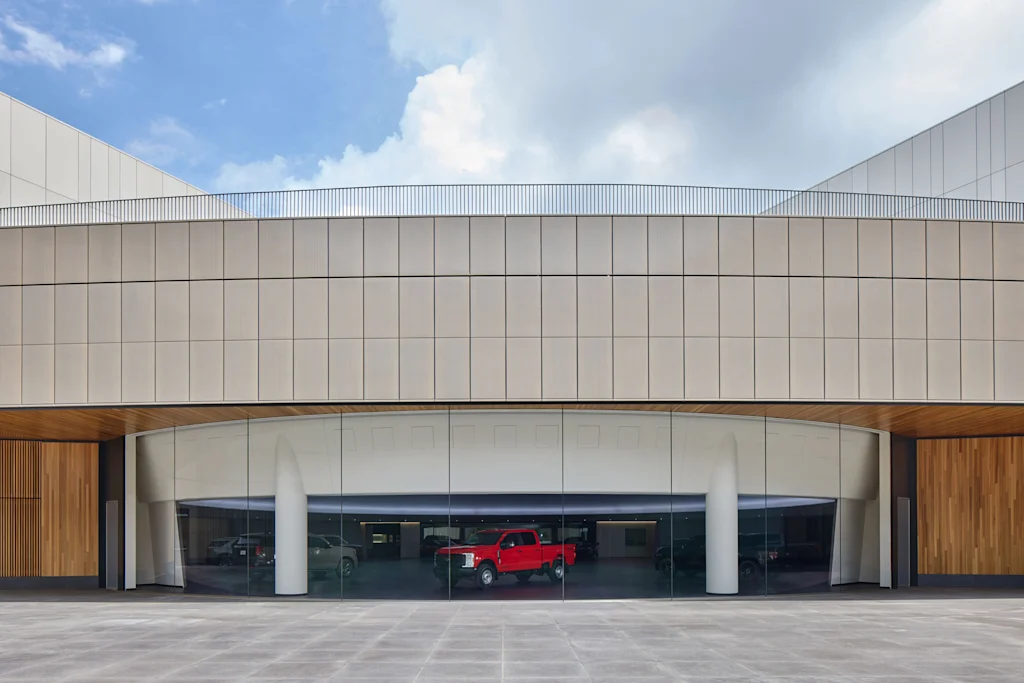

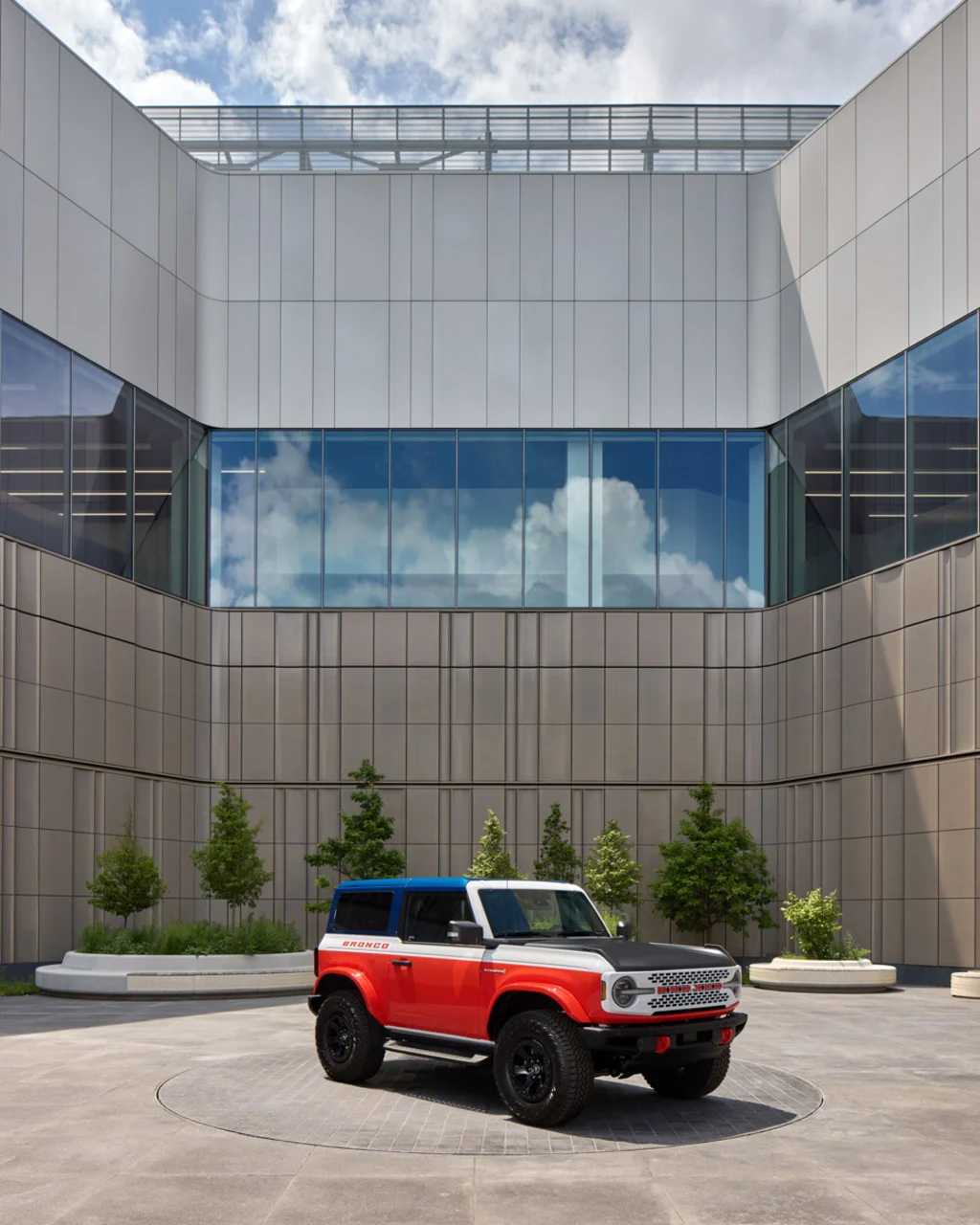
The design studios are also directly connected to an even more useful space: a large exterior courtyard where scale models and concepts can be given a good look in natural daylight. Elisangela Previte, global business operations manager for Ford Design, says the space makes it much faster for designers to vet their design choices, moving a model out of the controlled environment of the modern design studio and into the harsh glare of the sun. Though there are minor concerns about the potential for drone surveillance, the bigger concern is the geese that are trying to use the courtyard for their nest. Previte says they’re still trying to figure out the right way to keep the geese out.
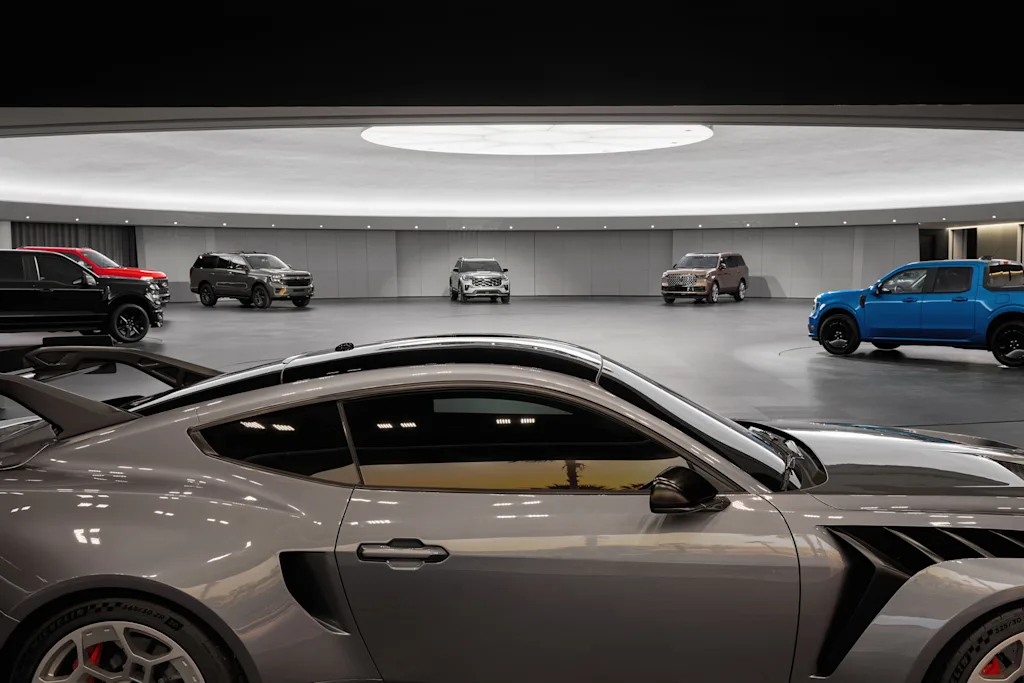

A quick ride in a freight elevator can bring a new model down to the building’s other prize space, a large domed showroom equipped with 10 in-floor turntables to slowly rotate cars, a large overhead light that can emulate light from any time of day, and a large conference room for executive meetings and new car reveals. The showroom also connects to its own courtyard, allowing those formal car design reviews to occur under natural light, and with the benefit of view lines that can stretch 180 feet. It’s the kind of space where the final approval for a new car model can come through or an emerging concept can be doomed to the archives.
Each step—from a design concept to a full-scale model to a new car approved for production—can feasibly all happen within this new headquarters building. It’s a radical concentration of abilities for Ford, marking a new approach for a company that can feel steeped in its own history, both for good and for bad. Given the pace of automaking, it will take time for consumers to see what impact all of this has on the cars that Ford produces. But for now, the building itself is a big indication of how the company sees itself evolving in the near term.

